Aircraft Maintenance Engineers (AMEs) play a critical role in ensuring the safety and airworthiness of aircraft. They are responsible for inspecting, maintaining, repairing, and certifying the functionality of various aircraft systems.
If you are interested in pursuing a career as an AME, this article will guide you through the necessary steps and provide information on where you can pursue AME courses and what are the requirements to become an Aircraft Maintenance Engineer (AME).
Step 1: Understand the Role of an AME

Before diving into the educational requirements, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of an AME’s responsibilities. AMEs are responsible for performing scheduled inspections, troubleshooting mechanical or electrical issues, and carrying out necessary repairs or replacements to maintain aircraft in optimal working condition.
They must comply with aviation regulations and safety standards to ensure the safety of passengers and crew members.
Step 2: Research and Choose a Specialization
AMEs can specialize in either mechanical (Category M or B1) or avionics (Category E or B2) maintenance. Mechanical AMEs focus on the physical components of an aircraft, including engines, airframes, and related systems. Avionics AMEs, on the other hand, specialize in electronic systems such as communication, navigation, and instrumentation.
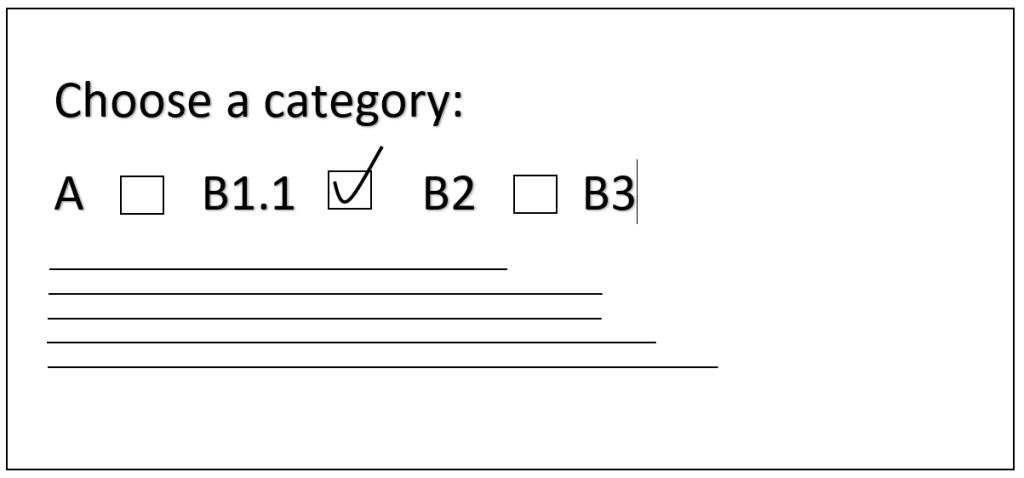
Consider your interests and aptitudes when choosing a specialization. There are also different categories of AME based on aircraft types. Category B1.1 is the license for the Mechanical AMEs for turbine powered aircraft while Category B2 for the Avionics or Electrical AMEs. Category A is the license for the line maintenance certifying staffs where B3 is for small aircraft maintenance license of aircraft below 2000 kg maximum take of weight.
Step 3: Enroll in an Accredited AME Program

To become an AME, you need to complete an approved Aircraft Maintenance Engineering program. These programs provide theoretical and practical training necessary to develop the skills required in the field. Research aviation institutes, colleges, or technical schools that offer AME courses. Ensure that the program you choose is approved by the appropriate aviation authority in your country.
For example, in European countries, the European Aviation Safety Agency approves (EASA) AME programs. In the United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) approves these courses for becoming aircraft maintenance engineers.
Every country has their own competent authority for ensuring civil aviation regulation is properly complied by the aircraft owners and organization and its associated personnel. Any individual training center or organization can be approved by its own competent authority and EASA or FAA.
Step 4: Meet the Eligibility Criteria
Eligibility criteria may vary depending on the country and aviation authority. However, some common requirements for enrolling in an AME program include:
- High school diploma or passing 12 grade schooling or equivalent qualification with a strong background in mathematics and physics.
- Your age requirement, usually 18 years or older.
- Fulfilling any medical fitness requirements specified by the aviation authority.
Step 5: Complete the AME Program

The duration of an AME program varies, but it typically takes 2-3 years to complete. The program consists of theoretical classroom instruction and practical hands-on training. You will learn about aircraft systems, maintenance procedures, regulations, safety practices, and troubleshooting techniques. Practical training may include working on real aircraft or using simulation equipment to gain hands-on experience.
You can find out the syllabus for different categories of licenses of AMEs from the part 66 regulations. These regulations and syllabus can be easily obtained from the competent authority website or just google it. Here is the link for Part 66 from EASA.
Step 6: Obtain the AME License/Certification
After successfully completing the AME program, you will need to pass the licensing examination administered by the aviation authority. If you have completed the AME course which is approved by the competent authority or EASA or FAA and have certain practical experiences, you can apply for the AME license to your competent authority or EASA or FAA.
In some cases if the competent authority wants they may ask you for an examination. The examination tests your knowledge and practical skills in aircraft maintenance. Upon passing the examination, you will receive an AME license or certification, allowing you to work as a qualified AME. But in most of the cases they do not go for examination as your completed AME course is already approved by them.
Step 7: Continual Professional Development
To stay current with evolving aviation technologies and regulations, AMEs should engage in continual professional development. Attend workshops,recurrent courses, conferences, and seminars, and stay updated with industry publications. This ongoing learning will help you enhance your skills and remain competitive in the field.
Conclusion
Becoming an Aircraft Maintenance Engineer requires a combination of education, practical training, and obtaining the necessary licenses or certifications. Research accredited AME programs offered by reputable institutions, and ensure they align with the requirements of the aviation authority in your country.
By following the outlined steps, you can embark on a rewarding career as an AME and contribute to the safety and efficiency of the aviation industry.




1 thought on “How to Become an Aircraft Maintenance Engineer (AME): A Path to Aviation Excellence”
Comments are closed.